Ovarian cancer is cancer that begins in the ovaries. The ovaries make female hormones and produce a woman’s eggs. Ovarian cancer is a serious cancer that is more common in older women. Treatment is most effective when the cancer is found early. Screening for ovarian cancer is not recommended for most women.
What is ovarian cancer?
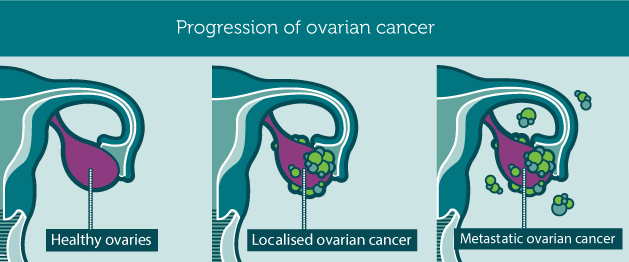
Ovarian cancer forms in tissues of the ovary. (An ovary is one of a pair of female reproductive glands in which the ova, or eggs, are formed.)
Tumors in the ovaries can be benign, which means they are not cancer, or they can be malignant, which means they are cancer.
Cancers that start in the ovaries can spread to other parts of the body. This is called metastasis. Cancer that starts in the ovaries and spreads to other parts of the body is still called ovarian cancer.
Who gets ovarian cancer?
Around one in every 60 women in the United States will develop ovarian cancer. Most ovarian cancers are diagnosed in women over 60, but this disease can also affect younger women. Among women in the United States, ovarian cancer is rare. Most ovarian cancers are diagnosed among women ages 55 to 64, but ovarian cancer can also affect younger women.
Are some women more at risk for ovarian cancer?
Women with a high risk of ovarian cancer are those with a harmful mutation on the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes. These mutations can be found with a blood test. Women with a family or personal history of breast or ovarian cancer also have a higher risk of ovarian cancer.
If you have family members in multiple generations with breast cancer or ovarian cancer, see your doctor to learn more about your risk of ovarian cancer. Research shows that certain steps, such as surgery to remove the ovaries and the fallopian tubes, may help prevent ovarian cancer in women who are at high risk. The sooner ovarian cancer is found and treated, the better your chance for recovery. But ovarian cancer is hard to detect early, because its symptoms are also the symptoms of many other illnesses.
What are the symptoms of ovarian cancer?
The following may be symptoms of ovarian cancer if they continue or get worse over time:
Pain in the pelvis or abdomen (belly)
Bloating in the abdomen
Urinary urgency (needing to pee right away)
Urinary frequency (having to pee often)
Constipation or diarrhea
Feeling full quickly while eating
Having difficulty eating
Vaginal bleeding or other discharge that is different than normal
Back pain
If you have any of these symptoms, talk to your doctor. He or she can determine if the cause is cancer or something else. Your doctor also may ask you to visit a gynecologic oncologist. This is a doctor who focuses on cancers of the female pelvis.
Should I be screened for ovarian cancer?
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends against screening women who are not at high risk for ovarian cancer. The USPSTF found that testing for ovarian cancer may do more harm than good. Current testing methods, like pelvic exams, ultrasound, and blood tests, can lead to “false positives” (results that say a woman has ovarian cancer when she really does not have ovarian cancer). These incorrect results can lead to surgeries that are not needed and that can be risky.
Some women, like those who are at high risk, can talk to their doctor about their risk and what they can do to help prevent ovarian cancer.